xfs_repair on LVM
Search for LVM information on all available hard drives and create all the needed entries in /dev so you can actually use them.
vgscan -v --mknodes
All recognizable LVM information were created under /dev/mapper You’ll probably see something like this:
$ ls -al /dev/mapper total 0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 100 Apr 13 13:49 . drwxr-xr-x. 20 root root 3100 Apr 13 13:49 .. lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Apr 13 13:49 centos-root -> ../dm-0 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Apr 13 13:49 centos-swap -> ../dm-1 crw-------. 1 root root 10, 236 Apr 13 13:49 control
The volume named centos-root is the logical volume that is mounted as the root partition.
Activate your volumes:
vgchange -a y
Repair the XFS filesystem:
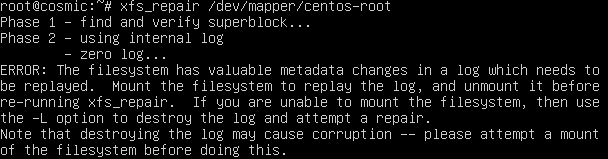
xfs_repair /dev/mapper/centos-root
You may receive an error stating there is an unwritten (dirty, corrupt) log. As this note from RedHat states, you may have data loss if you clear the log.
The
xfs_repairutility cannot repair an XFS file system with a dirty log. To clear the log, mount and unmount the XFS file system. If the log is corrupt and cannot be replayed, use the-Loption (“force log zeroing”) to clear the log, that is,xfs_repair -L /dev/device. Be aware that this may result in further corruption or data loss.
If you can’t mount the volume and clear your log, you will have to use -L and risk data loss.
 I haven’t experienced any serious data loss after using
I haven’t experienced any serious data loss after using -L, or if I did, it wasn’t apparent to me. ** Use at your own risk **